Each living organism is composed of the basic unit of life, i.e., the cell. Though there are different cell types (oval, round, cylindrical), they have the same structural organization.
Protective outer covering lines each cell called the cell membrane, which holds the cytoplasm fluid. The cell membrane is bilayer in nature and is made up of phospholipids. The bilayer makes it polar at one end and nonpolar at the other. That facilitates selective absorption of particles in and out of the cell. The cytoplasm, also called cytosol, maintains and carries out all the cell's vital functions through its organelles.
Both the prokaryotes (primitive forms) and eukaryotes have cell organelles. But eukaryotes have well-developed cell organelles. Cell organelles are sub-cellular structures that do compartmentalization and serve different functions. They not only serve several functions but also hold the cytoplasm intact.
Nucleus, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic reticulum, Ribosomes, Lysosomes, and Peroxisomes are examples of cell organelles.
Scanning electron microscopy image showing the structure of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi (G), and Mitochondria (M).
What Does The Endoplasmic Reticulum Do And Its Functions?
Most (50%) of the membrane surface is provided by the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell. It is found only in eukaryotes (plants and animal cells) and significantly produces lipids and proteins. K.R. Porter first observes them.
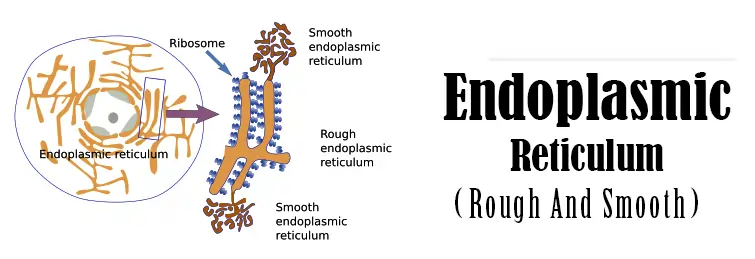
It is a complex and large structure in the cytoplasm and spans between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Its large and dynamic structure assigns several critical roles like calcium storage, lipid (fats) and protein synthesis, transport, and protein folding. Each structure is composed of three elements. i.e., tubules, sheets, and the nuclear envelope.
The endoplasmic reticulum comprises a group of interconnected sac-like structures called tubules. These tubules collectively modify and produce proteins and lipids. It is a bilayer in structure, i.e., covered by a protective membrane. This membrane has its origin in the nucleus.
Based on the function and presence of ribosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum is classified into two types, rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER). These are the parts of Biology.
Both these forms are present in both plant and animal cell types. Though there are two types, they appear together and coordinate cell activities.
Based on the presence and absence of ribosomes in their structure, they are divided into rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulums, respectively. As such, cell types involved in protein synthesis are rich in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and the cell types assigned to produce lipids are more in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
What Does Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Do In A Cell & Its Definition?
They are made up of flattened convoluted sac-like structures sealed at both ends. These structures form the connective structures between the nucleus and cell membrane. As such, they do share their lipid bilayer structure. As mentioned, they are studded with ribosomes on their cytosolic face, i.e., towards the open end. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is distributed throughout the cell but mainly concentrated around the nucleus and Golgi bodies.
The Role Of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- Ribosomes are called protein factories of the cell as they synthesize the proteins during translation. As these ribosomes are studded on the RER, the rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site of protein synthesis.
- The RER, in coordination with ribosomes, aids in translocating the polypeptide chains and amino acids into their lumen and sorts out the proteins. In other words, the polypeptides assembled in the cytoplasm will be sorted and labelled with peptide signalling ensuring they are transported to the right place and does the right function. This peptide signal decides the fate of the protein.
- The proteins produced are given an identity within the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The proteins taken into the lumen will be modified and folded, giving them the essential structural identity. As such, the proteins become eligible for the lock and fundamental principle.
- They are also called the quality control department. Protein sorting out takes place in the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The proteins folded are absorbed or rejected based on whether they are folded correctly or incorrectly. Once accepted, they are translocated to the Golgi bodies for finishing.
The structure of the Endoplasmic reticulum shows SER and RER.
What Is The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Made Of & Its Definition?
The absence of the ribosomes on the structures confers the name smooth to the endoplasmic reticulum. As such, the cell types involved in lipids production are rich in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. They also have the same structure as RER, but the tubules are more tubular with fewer convulsions. They are distributed all over the cytosol.
The Role Of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- They are sites of production of lipids.
- They sometimes help in the metabolism of lipids and their allied products.
- It also aids in synthesizing steroid hormones in most endocrine glands (Adrenal glands).
- Glycogen is stored as blisters on the surface of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. SER breaks down these glycogen molecules into glucose to release energy (especially in liver cells).
- It also reduces the toxification of several organic chemicals from the cytoplasm. SER breaks down harmful organic chemical moieties into more specific water-soluble components, making them safe for the cell.
- Liver cells, usually called detoxifying organs, are rich in this smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Alcoholic compounds, which are either consumed directly or produced as end products from food, need to be detoxified from the body. The liver takes the lead in doing so. In doing this function, the SER sometimes doubles its surface area to overcome the load of alcohol and other poisonous compounds.
- Muscle contraction takes place with the help of calcium ions. And such ions are released by the SER, helping the muscles in contraction.
To conclude, ER is an important cell organelle that takes most of the workload next to the nucleus. They carry protein synthesis and lipid synthesis, and some other critical functions. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum also detoxifies some of the harmful drugs that are usually intake during diseases. And also, if you need efficient assignment help on Biology or any other subject, please get in touch with EssayCorp.