From the beginning, we all studied the definitions of our beloved topic, i.e. Matter. But now it’s time to get your attention on the overview of this essential chemistry aspect.
What is Matter? Explain With Examples.
In the simplest term, Matter is any tangible object occupying space and having mass. In today’s world, everything is made up of Matter. To understand more clearly, let’s take some examples of properties of Matter in science. Like cars, paper, tables, people and computers etc. As these objects contain space and mass. However, ideas, imagination and emotions are not included in the classification of Matter as these things don’t have any group or distance.
How many different states of Matter are there?
There are different types of Matter and its properties in various forms. These general properties of Matter are listed below:
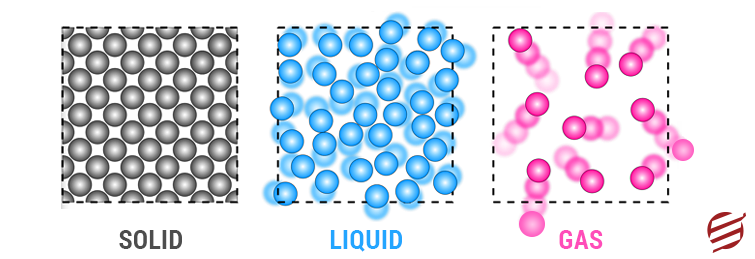
Solids: One of the most critical states among all matter properties, i.e. Solids. In this Property of Matter, particles are very tightly packed together so that they arecannotve much. In the case of solids, they do not adapt to the shape of the holder in which they are positioned. The most striking characteristics of solid Matter are as follows:
-
- They have a definite shape
-
- They have a fixed volume
- The elements are so closely and firmly filled together that even increased pressure would not allow solids to compress.
For example, steel, brick, rock, apple, copper, brass, wood, etc.

Liquids: Another state of Matmatterequently asked in the examination, i.e. Liquids. In this phase, the particles present have more kinetic energy than solids. Furthermore, the liquid elements are not seized in a fixed arrangement but are somewhat close to each other. Having an indefinite shape, the details of the liquid have enough space to move around each other. But, in the case of Liquids, they cannot be compressed like solids.
For example, water, milk, honey, coffee, urine, blood, etc.

Gases: Compared to solids and liquids, the particles in the gas matter have space between them with high kinetic energy and low density. Gases have no fixed shape or volume. In this state of Matter, the atoms move verily, causing them to spread out and diffuse. When other gas particles enter a holder, they become compressed.
For example, air, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, water vapour, nitrogen, helium, etc.
How many different states of Matter are there? However, apart from these three properties of Matter, some other properties of Matter make this topic more fascinating than any other.
1. Plasma: Plasma is a general state of Matter in the worse. It contains highly charged particles with highighernetic energy andn any other form of Matter. It also holds noble gases (argon, neon, helium, krypton, radon and xenon) that make blooming signs by ionizing them to the plasma state.
Examples are Lightning, solar wind, a comet tale, and a nuclear explosion fireball.
2. Bose-Einstein Condensates: This low-energy state of Matter is derived from the names of Satyendra nath bose and Albert Einstein. It contains particles having a similar quantum state. Or in other words, it comprises a dilute gas of bosoms cooled to zero temperature.
Examples: Superconductors and Superfluids.

Changing States of Matter
After discussing the different properties of Matter, now it’s time to get on another interesting topic, i.e. changing states or phases. The change in Matter may sometimes require high pressure, temperature and energy. However, there are six phases in which different substances react differently to varied temperatures. These unprecedented changes are as follows:
- Freezing: This change of Matter arises when a substance changes from liquid to solid at an extreme temperature, such as Water to ice.
- Condensation: In this type of state change, the substance changes from gas to liquid. For example-After, after a hot shower, the Water collects on the bathroom mirror.
- Melting: This change of Matter occurs when a substance changes back from solid to liquid, for example-Ice to, to Water.
- Vaporization: This state change occurs when a substance changes from liquid to gas. It can only happen from boiling or evaporation, for example-Boiling, Water.
- Sublimation: In this phase, the solid is directly transformed into a gas without going through a liquid stage. This whole process is known as sublimation, for example-Dry, ice.
- Deposition: Often known as De-sublimation. It happens when the gas converts directly into a solid, wintering the liquid phase, such as changing water vapour into ice.

If you understand the subject better, you can do your assignments perfectly. But students who face trouble in doing chores can reach Essaycorp for all assignment help. We have a team of experts that will help you in achieving the best grades.