Microeconomics study is the branch of economics that deals with individual units like a person, firm, household, or industry. Microeconomics is primarily concerned with the elements that influence an individual’s decision making and what are the implications of the decisions that the individuals make. It also studies the determination of price and demand in a market. The major theories studied under microeconomics are demand, supply, and market equilibrium, elasticity, consumer and producer surplus, scarcity, possibility, opportunity cost, production decision and economic profit, and forms of competition.
Concepts Of Microeconomics :
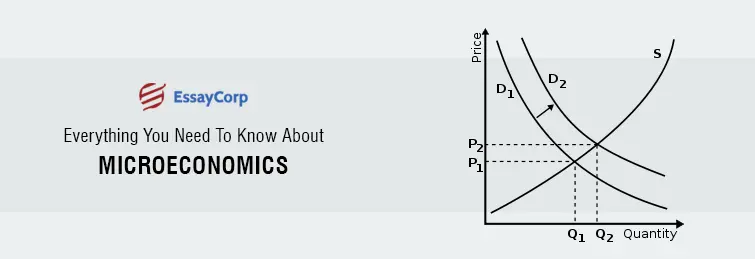
1. Demand – It is the economic concept that explains the price a consumer is willing to pay for the purchase of goods and services. Assuming all economic elements constant, a rise in the price of a good or service will lead to a fall in the demand and vice versa. Every organization or business employs economists who try to predict the most accurate demand for the products of the company in the market, failure to make the estimation can lead to loss or wastage of product – depending on the nature of the goods.

2. Supply And Market Equilibrium – Supply is an economic concept that often is paired with demand because of their causal relationship. Supply is the quantity of goods and services that is available to the consumers for purchase. All economic indicators remain constant then the rise in the price of a product will lead to rise in supply as every producer will look to maximize their profit.
Market equilibrium is the point where both the forces of demand and supply become equal. That is the supply of goods equals the demand in the market. The effect of this is that the price becomes stable.

3. Elasticity – It is the change in the price of one variable due to the change in the price of the other. Elasticity can be defined as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price. A product is considered to be elastic if the change in quantity demanded also brings a change in the price. A product is said to be inelastic if the change in price does not affect the demand. For example – the products like alcohol, petroleum, etc. have very minimum effect of the rise in price, therefore they are inelastic goods.
4. Consumer And Producer Surplus – The consumer surplus is a situation when the price of the product is less than what the consumer is actually willing to pay for it. This concept was developed to measure the benefits to the public from the creation of highways, bridges, and canals. This theory is based on marginal utility.
Producer surplus is the difference between the minimum price that the producer is willing to accept and the actual price they receive from the market. The minimum price is the cost of production and the surplus is the difference between the cost of production and the selling price.

5. Scarcity – This is the primary economic problem that economics explains. Scarcity is the abundance and never ending necessity of the population and the limited quantity of resource available to satisfy this need. The theory of scarcity explains that if a product is in limited quantity and the demand for the product is high then the price of the product will be high. The consumer must decide if the benefit from purchasing the product outweighs the huge cost.
6. Opportunity Cost – It is the cost of choosing one course of action over the other. An opportunity cost is the cost incurred for choosing to make investment on one thing while sacrificing the other. The formula for calculating opportunity cost is “Return of most lucrative option minus the return of chosen option.”
7. Forms Of Competition – There are mainly four types of competition in the market – perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. In a perfect competition the price of goods and services is determined by the forces of demand and supply and there are a large no. of sellers, there is very little barrier for a company to enter this market.
Like the perfect competition, in a monopolistic competition also there are many sellers. But the difference is that they sell different products; the products sold differ slightly but they serve the same purpose.
The word oligopoly in itself means few sellers. In this form of market each seller owns a huge portion of the market and the cost of entering the market is very high limiting the number of sellers. Companies in this form of market are usually airlines companies, and automobile companies.
If you observe the number of sellers and the degree of competition, monopoly is exactly the opposite of perfect competition. There are several small companies in a perfect competition but only a few companies in a monopoly. In a monopoly, the price of the product is not determined by market force but by the company.
Conclusion :
The theory of microeconomics is very important as they form the base of macroeconomics. Its study is very important as it helps an economist or a company determine the need of the people and can analyze its capability to fulfill the demand. The concept of microeconomics is often considered to be more convoluted than macroeconomics.